| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | MOQ | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Huile essentielle de Cannelle Ecorces - 30 gr | - |
Visit website
|
- | - | - | - | - | |
|
|
CINNAMON Rectified Essential Oil | M_0058821 |
Visit website
|
Naturel | - | - | - | - | |
|
|
CINNAMON LEAF EO | 4410000028 |
Visit website
|
Naturel | - | Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume | Leaves | Sri Lanka | |
|
|
CANNELIER | N225 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle |

|
- | Cinnamomum verum J.Presl | Rameau | Madagascar |
|
|
CANNELIER | B225 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle |

|
- | Cinnamomum verum J.Presl | Rameau | Madagascar |
|
|
CINNAMON LEAF EO | - |
Visit website
|
- | 10 grs | - | - | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° :
8015-91-6 -
EINECS number :
84649-98-9 -
FEMA number :
2292
-
Volatility :
Heart/Base -
Price Range :
€€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Appearance :
Colorless liquid -
Density :
1,037 - 1,053 @20°C -
Refractive Index @20°C :
1.527 - 1.540 @20°C -
Optical rotation :
-2,5° // +2° -
Vapor pressure :
Data not available. -
Flash Point :
Data not available. -
Acid Value :
Botanical informations
Botanical name :
zeylanicum
Botanical profile :
The cinnamon tree is a tree of the Lauraceae family and the Cinnamomum Schaeff. genus.
Chemotypes :
There are more than 400 species in the Cinnamomum Schaeff. genus.
Cinnamomum verum J.Presl : Ceylon cinnamon EO. Leaves are extracted.
Cinnamomum cassia (L.) J.Presl :Chinese cinnamon or Cassia EO. Leaves from this tree are not extracted for perfumery.
We can also distinguish :
Cinnamomum burmanni (Nees & T.Nees) Blume : Korintje cassia SFE and Cinnamomum tamala : Indian cinnamon, much less cultivated.
Cinnamomum camphora (L.) J.Presl CT Linalol: Hô wood EO - This chemotype contains more than 80% linalool. The natural Linalol is mainly extracted from it.
Cinnamomum camphora (L.) J.Presl CT Cineol: Ravintsara EO - This is the chemotype we are studying here.
Cinnamomum camphora (L.) J.Presl CT Camphor: Camphor tree EO - This chemotype contains between 50% and 70% Camphor.
Cinnamomum tamala (Buch.-Ham.) T.Nees & Eberm : From India, very low volume.
Cinnamomum parthenoxylon (Jack) Meisn. : Siam wood oil
Extractions & Uses
Extraction process :
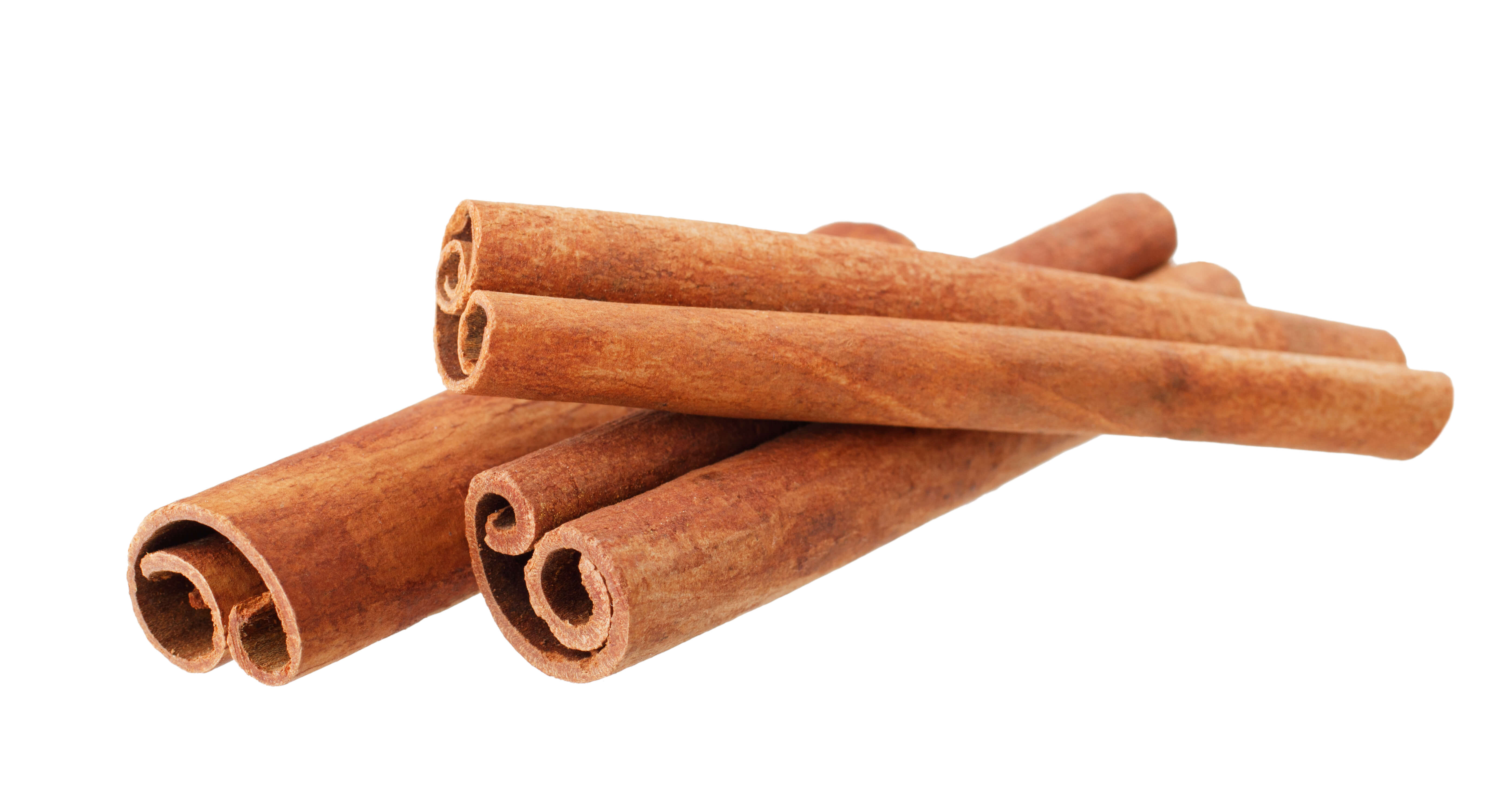
The cinnamon tree is up to seven meters tall. Several parts of this tree can be extracted to obtain essential oils. When dried, the bark gives the commonly used cinnamon sticks and the leaves measures seven to eighteen centimetres long.
The leaves and the bark are mature 12 to 18 months after the preceding harvest. From red to dark green, the colour of the leaves indicates the cinnamon maturity. The culture often takes place in May and November. The leaves are collected by cutting the twigs off the tree and separating the leaves from the branches. The leaves are ground and dried before they are extracted by steam distillation.
About 1 hectare of cinnamon forest allows to cultivate 1 ton of leaves, offering a yield of 2.5 to 3 kg of essential oil (extraction yield: 0.3%).
Uses in perfumery :
Useful in spicy notes and as a modifier in amber perfumes.
Stability :
Aromatic compounds can be chromophoric and cause a coloration of the oil, especially in alkaline bases
Major Components :
- Eugenol (70 - 83%)
- Benzyl benzoate (2 - 4%)
- Cinnamyl acetate (1,1 - 1,8%)
- Cinnamaldehyde (0,8 - 1,5%)
- Eugenyl acetate (1,3 - 3%)
- Safrole (≈1%)
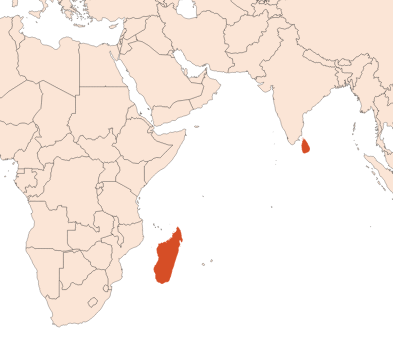
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Other comments :
The smell of the leaf is different from the bark as it is closer to clove (high rate of Eugenol) than cinnamon.
Its essential oil is one of the precursors of the extraction of natural Eugenol, which can be used for the synthesis of Vanillin.
The essential oil of cinnamon leaf is less expensive than the cinnamon bark one.
Cinnamon roots can also be extracted. Their essential oil is more camphorated, earthy and floral.
IFRA
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is restricted by the 51th amendment