Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | MOQ | Purity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Menthone - 30gr | - |
Visit website
|
- | - | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° :
89-80-5 -
EINECS number :
201-941-1 -
FEMA number :
2667 -
FLAVIS number :
07.176
-
JECFA number :
429 -
Volatility :
Head -
Price Range :
€€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Appearance :
Colorless liquid -
Density :
0,895 -
Refractive Index @20°C :
1.448 - 1.453 -
Optical rotation :
Data not available. -
Vapor pressure :
Data not available. -
Flash Point :
79°C (174,2°F)
-
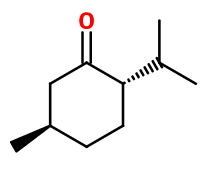
Molecular formula :
C10H18O -
Molecular Weight :
154,25 g/mol -
Log P :
3,05 -
Fusion Point :
-20°C (-4°F) -
Boiling Point :
209°C (408,2°F) -
Detection Threshold :
170 ppb (0,000017%)
Chemistry & Uses
Uses in perfumery :
Menthone is used in minty notes, for a deep and liquorice note. Allows to nuance the cold sensation of L-Menthol and L-Carvone in a mint reconstitution. Gives a very sweet and frosty mint effect.
Year of discovery :
Data not available.
Natural availability :
The natural production of Menthone can be made from a dementholised Corn Mint EO (see L-Menthol).
Isomerism :
Menthone is a mixture of two pairs of dextrorotatory and laevorotatory isomers: Menthone and Isomenthone. Isomenthone has a more moldy smell than Menthone. These two enantiomers have a strong tendency to interchange, making it difficult to separate them from synthetic Menthone or from an essential oil. In the synthesis of Menthone, the isomers of the molecules can be selected by changing the synthesis conditions or the starting reagent (for example, dehydrogenated or oxidized L-Menthol gives a mixture of L-Menthone and D-isomenthone). Linalool, Nerol, Geraniol and Terpineol are some of the constitutional isomers of Menthone. Nevertheless, they have a much more floral or terpenic smell, far from the frosty mint note of Menthone.
Synthesis precursor :
Menthone is a precursor to the synthesis of Menthol by catalytic hydrogenation, forming NeoMenthol and Menthol.
Synthesis route :
Synthetic Menthone is produced by a dehydrogenation of L-Menthol, with the presence of catalytic copper and chromium. A hydrogenation of Thymol, catalysed by palladium, also allows to obtain a racemic mixture of Menthone isomers.
Stability :
Stable in perfumes and diverse functional bases
IFRA
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is not restricted for the 51th amendment