| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | MOQ | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Huile essentielle de Thym rouge - 30 gr | - |
Visit website
|
- | - | - | - | - | |
|
|
THYM LINALOL | B915 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle |

|
- | Thymus vulgaris L | Sommité fleurie | France |
|
|
THYM THUYANOL | B920 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle |

|
- | Thymus vulgaris L | Sommité fleurie | France |
|
|
THYM THUYANOL | 920 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle | - | Thymus vulgaris L | Sommité fleurie | France | |
|
|
THYM THYMOL | B925 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle |

|
- | Thymus vulgaris L | Sommité fleurie | France |
|
|
BENZOIN TR 75-83% ALCOHOL | 442FP24777 |
Visit website
|
Natural Extracts and Oils |

|
- | - | - | UK |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° :
8007-46-3 // 84929-51-1 -
EINECS number :
284-535-7 -
FEMA number :
Donnée indisponible.
-
Volatility :
Heart -
Price Range :
€€€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Appearance :
Green liquid -
Density :
0,910 – 0,937 @20°C -
Refractive Index @20°C :
1.494 - 1.504 @20°C -
Optical rotation :
−6° // 0° -
Vapor pressure :
Data not available. -
Flash Point :
Data not available. -
Acid Value :
Botanical informations
Botanical name :
Thymus vulgaris L.
Synonyms : Origanum thymus Kuntze // Thymus collinus Salisb.
Botanical profile :
Red thyme belongs to the Lamiaceae family and the genus Thymus L.
The Lamiaceae family is the most important family in perfumery, notably including lavenders, basils, mints, sages, rosemaries, patchoulis, and thymes.
Chemotypes :
The genus Thymus L. comprises about 570 different species and a very large number of chemotypes. Among the main chemotypes, we can highlight:
Thymol chemotypes:
- Thymus vulgaris L.: Thyme oil (red), the most widely used as it is very economical and allows the isolation of many compounds of interest.
- Thymus zygis L.: Spanish Thyme, rich in thymol or linalool.
Eucalyptol chemotypes:
- Thymus mastichina (L.) L.: Thyme oil(white) , two species also widely used.
Other notable Thymus species:
- Thymus saturejoides Coss.: Savory Thyme (Thyme satureioide oil (borneol type) – rich in borneol and carvacrol, found mainly in northern Morocco.
- Thymus serpyllum L.: Wild Thyme, with numerous chemotypes.
- Thymus capitatus (L.) Hoffmanns. & Link: Cretan Thyme, rich in carvacrol or thymol.
- Thymus pulegioides L.: Thyme rich in pulegone.
This list is not exhaustive, as thyme has undergone countless crossings throughout its history.
Extractions & Uses
Extraction process :
Thyme is a herbaceous plant that reaches up to 30 cm tall. Its fragrant principle is contained in its stems, but especially in its leaves, which are only one centimetre long. In Spain, almost all cultures are wild. The propagation of a thyme culture is done by sowing seeds. Cutting methods are also used. Also, a few tens of centimetres must be left between the plants to guarantee a better quality of the essential oil and a better extraction yield. The plants need a lot of sun exposure. The culture starts when the plant blooms (the flowers are white as reflected by the name of this thyme).
In cultivation, the leafy stems of thyme are mowed or hand picked to be dried for a few hours under 104 °F. In Spain, cultivation takes place from February to August. In France, this cut is made twice a year: the first one in May and the other one around September. However, it is also possible to find crops with one cut and others with three.
A steam distillation under pressure for 1.5 hours allows to collect an essential oil at the refrigerant outlet by decantation of the water. The extraction yield is between 1.5 and 2.5%.
Volatile solvent extraction provides an extraction yield of about 0.3%.
Uses in perfumery :
Gives an aromatic and sunny touch to woody, chypre and fougere compositions.
Stability :
Aromatic compounds can be chromophoric and cause a coloration of the oil, especially in alkaline bases
The terpenes identified in this raw material can polymerize when they are oxidized
Major Components :
- For a Thymol chemotype :
- Thymol (70 - 80%)
- p-Cymene (5 - 15%)
- Gamma-terpinene (5 - 10%)
- Carvacrol (1 - 5%)
- Linalool (1 - 5%)
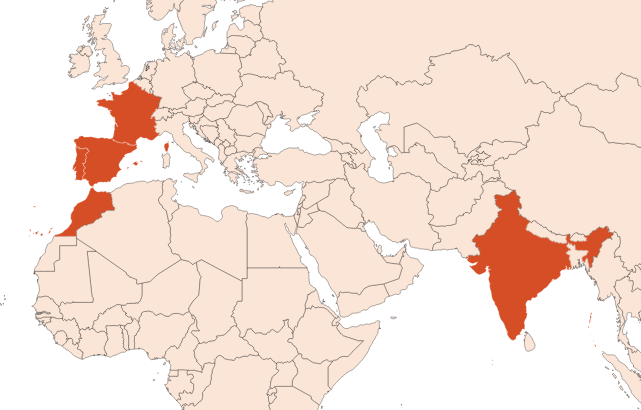
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Other comments :
The name given to thymes is representative of the colour of their flowers. For red thyme, they are red-violet. Red thyme is also consumed regularly in the mediterranean cuisine.
As a pioneer, thyme prepares soils to welcome genette, junipers and oaks.
Red thyme is the main precursor of natural Thymol, its major component.
The quality of thyme and its essential oil is subject to compliance with ISO standards imposed by the AFNOR (French Association of Standards). These standards relate to the physical and chemical characteristics of the plant and oil. Even though, adulteration is possible with synthetic Thymol or Eucalyptol or ajowan essential oil. This practice is less common than before.
IFRA
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is not restricted for the 51th amendment