| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | MOQ | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Huile essentielle de Bergamote - 30 gr | - |
Visit website
|
- | - | - | - | - | |
|
|
BERGAMOT Essential Oil | M_0020356 |
Visit website
|
Naturel | - | - | - | - | |
|
|
BERGAMOT Rectified Essential Oil | M_0063590 |
Visit website
|
Naturel | - | - | - | - | |
|
|
BERGAMOTE | B120 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle |

|
- | Citrus bergamia Risso et Poiteau | Zeste | Italie |
|
|
BERGAMOTE SANS BERGAPTENE | B123 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle |

|
- | Citrus bergamia Risso et Poiteau | Zeste | Italie |
|
|
BERGAMOT OIL BPC 1949 | 442FP23263 |
Visit website
|
Natural Extracts and Oils |

|
- | - | - | UK |
|
|
BERGAMOTE CRUDE ITALIA EO | - |
Visit website
|
- | 10 grs | - | - | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° :
8007-75-8 -
EINECS number :
296-429-8 -
FEMA number :
2153
-
Volatility :
Head -
Price Range :
€€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Appearance :
Pale yellow to green liquid -
Density :
0,876 - 0,883 -
Refractive Index @20°C :
1.465 - 1.470 @20°C -
Optical rotation :
-
Vapor pressure :
0.4 mmHg @20°C -
Flash Point :
54°C (129.2°F) -
Acid Value :
Botanical informations
Botanical name :
Citrus ×limon (L.) Burm.fil.
Synonyms : Citrus aurantium subsp. bergamia (Risso) Wight & Arn. // Citrus aurantium var. bergamia (Risso) Brandis
Botanical profile :
Bergamot is the fruit of the bergamot tree, which belongs to the Rutaceae family and the Citrus L. genus.
The Rutaceae family includes all citrus fruits, as well as buchu and amyris.
Chemotypes :
The Citrus L. genus, which includes the vast majority of citrus fruits, contains a large number of varieties used in perfumery:
- Citrus × aurantium L.: Bitter orange tree, cultivated in Spain and Florida. Orange oil expressed (Bitter) / Orange oil (Bitter) / Petitgrain bigarade oil / Petitgrain bigarade absolute / Petitgrain oil (Paraguay) / Orange flower absolute (Bitter) / Orange flower concrete (Bitter) / Orange flower SFE (Bitter)
- Citrus × aurantiifolia (Christm.) Swingle: The lime tree, mostly cultivated in Mexico. Lime oil expressed / Lime oil distilled
- Citrus × bergamia Risso: The bergamot tree, a hybrid of lemon and bitter orange, cultivated for its fruit and petitgrain oils. Bergamot oil expressed / Petitgrain bergamot absolute.
- Citrus hystrix DC.: Kaffir lime, grown in Thailand and India. Kaffir lime oil.
- Citrus × junos Siebold ex Yu.Tanaka: Yuzu, produced in Japan and Korea. Yuzu oil / Citrus junos oil / Citrus junos extract
- Citrus × limon (L.) Burm.fil.: The lemon tree, cultivated in Italy for its fruit and leafy branches. Lemon oil / Lemon oil (distilled, rectified) / Petitgrain lemon oil
- Citrus × paradisi Macfad.: The grapefruit tree, of Malay origin, cultivated in Brazil and Israel for its fruit’s essential oil. Grapefruit oil / Grapefruit flower oil / Grapefruit oil expressed
- Citrus sinensis L.: The sweet orange tree, widely cultivated in Brazil and California, is the most used citrus in perfumery. Orange flower absolute (Sweet) / Orange flower concrete (Sweet) / Orange flower SFE (Sweet) / Orange cold pressed (Sweet)
- Citrus reticulata Blanco: The mandarin tree, especially cultivated in Italy for its fruit and petitgrain (leaf oil). Mandarin oil (red) / Mandarin oil (yellow) / Mandarin oil (green) / Petitgrain mandarin oil. Its hybrid with sweet orange gave rise to the clementine (Clementine oil).
- Citrus medica L.: The citron tree, grown in Sicily. Citron oil.
Extractions & Uses
Extraction process :
Bergamot comes from the bergamot tree. First green then yellow, it is a citrus of about 80 to 200 grams. The harvest, done by hand (fruits are very sensitive), begins in November and ends around the end of January. The bergamots are stored for 2 to 3 days to warm them and soften the zest.
After that, the fruit is put in a sfumatrice to extract the essential oil (cold expression). The sfumatrice works by pricking all the zest of the fruit with needles in order to collect the essential oil and the zest debris. Then these two parts are washed away by a stream of water to a centrifuge. The purpose is to separate the oil from the water and the debris from the peel. Once this separation is done, the essential oil of raw bergamot is collected. The oil can also be obtained by separating the zest of the fruit in a peeler machine and by steam distilling the zest. This essential oil is called ''distilled bergamot '' or ''Cold expressed Bergamot ''.
The cold expression yield is approximately 0.5%.
An extraction with a volatile solvent gives a yield of 4%. The essential oil must be rectified to remove the bergaptenens, which are photosensitizers. This rectification can also be used to isolate terpenes or other compounds from the bergamot.
The oul quality varies according to the harvest months: more floral in November (higher presence of linalool) and cooler in January (higher presence of linalyl acetate). There is also a ''black bergamot '' which is an extraction of the zest of an overripe fruit fallen from the tree during the winter whose zest has become black.
Uses in perfumery :
Used in eaux fraîches, colognes, chypre accords (with Bergamote EO, Patchouli EO, Cistus EO, Cistus Labdanum Absolute Green and Oak Moss Absolute). Brings freshness to the head and lightens oriental notes.
Stability :
Solubility issues in perfumes
Citruses tend to fade through time in perfumes
Limonene tends to convert into Carvone through time, and to give a minthy note to the oil
The esters identified in this raw material can form their corresponding acid in stability tests
The terpenes identified in this raw material can polymerize when they are oxidized
Major Components :
- D-Limonene (30 - 45%)
- Linalyl acetate (22 - 36%)
- Gamma-terpinene (6 - 10%)
- Beta-pinene (5,5 - 9,5%)
- Linalool (3 - 15%)
- Beta-bisabolene (0,3 - 0,55%)
- Geranial (0,25 - 0,5%)
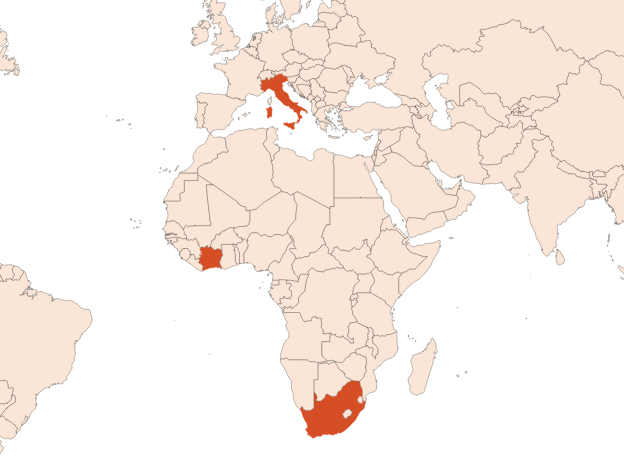
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Other comments :
The essential oil of bergamot is often called ''bergapten-free '' as the oil used in perfumery can only be used once all the bergaptenes has been removed.
Citrus currently suffer from a disease called ''citrus greening ''. This disease is deadly for citrus fruits and no treatment exists. It is transmitted by a vector insect that attacks young shoots: the psylla. This results in the premature death of many trees and therefore the decline in the general production of the essential oil and its quality (reduction of the Limonene level).
IFRA
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is restricted by the 51th amendment
- Quantitative limit on the use :
-
Cat.1 Cat.2 Cat.3 Cat.4 Cat.5A B C DCat.6 0,4 % 0,4 % 0,4 % 0,4 % 0,4 % 0,4 % 0,4 % 0,4 %0,4 % Cat.5A B C DCat.6 0,4 % 0,4 % 0,4 % 0,4 %0,4 % Cat.7A BCat.8 Cat.9 Cat.10A BCat.11A BCat.12 No Restriction 0,4 %0,4 % No Restriction No Restriction 0,4 %No Restriction 0,4 %No Restriction Cat.10A BCat.11A BCat.12 No Restriction 0,4 %No Restriction 0,4 %No Restriction
-
Restricted ingredients due to phototoxicity considerations: notes
The Standard is set due to the phototoxic effects of Bergamot oil expressed. For more detailed information on the application of this Standard, please refer to the note on phototoxic ingredients in Chapter 1 of the Guidance for the use of IFRA Standards. If the level of furocoumarins is unknown, the restriction level specified in this IFRA Standard applies. Combination effects of phototoxic ingredients are only taken into consideration for the furocoumarin-containing fragrance ingredients (extracts) listed in the IFRA Standard of Citrus oils and other furocoumarins containing essential oils. If combinations of furocoumarin-containing phototoxic fragrance ingredients (extracts) are used, the use levels must be reduced accordingly. The sum of the concentrations of all furocoumarin-containing phototoxic fragrance ingredients (extracts), expressed in of their recommended upper concentration level in the consumer product shall not exceed 100. For qualities of the expressed oil in which the less volatile components have been concentrated by partial or total removal of the terpene fraction, this limit should be reduced in proportion to the degree of concentration.