Photo credits: ScenTree SAS

Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | MOQ | Purity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
SYRINGA ALDEHYDE (50%) | ALS-1 |
Visit website
|
- | 10 grs | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° :
104-09-6 -
EINECS number :
203-173-2 -
FEMA number :
3071 -
FLAVIS number :
05.042
-
JECFA number :
1023 -
Volatility :
Heart -
Price Range :
€€€€€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Appearance :
Colorless liquid -
Density :
1,032 -
Refractive Index @20°C :
Donnée indisponible. -
Optical rotation :
Donnée indisponible. -
Vapor pressure :
Donnée indisponible. -
Flash Point :
70°C (158°F)
-
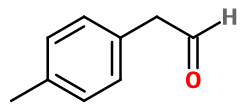
Molecular formula :
C9H10O -
Molecular Weight :
134,18 g/mol -
Log P :
2,21 -
Fusion Point :
Donnée indisponible. -
Boiling Point :
-
Detection Threshold :
Donnée indisponible.
Chemistry & Uses
Uses in perfumery :
Syringa Aldehyde is used for mimosa accords, and for its honey and powdery facet in floral notes, also bringing an animalic facet.
Year of discovery :
Data not available.
Natural availability :
Syringa Aldehyde is found in corn oil in small quantity, not allowing to use dit in its natural state.
Isomerism :
Syringa Aldehyde has two positional isomers : ortho-methyl benzyl acetaldehyde and meta-methyl benzyl acetaldehyde. Both are not used in perfumery. Syringa Aldehyde also is a constitutional isomer of Cinnamic Alcohol, although it does not have the same smell.
Synthesis precursor :
Syringa Aldehyde is not used for the synthesis of another compound of olfactive interest.
Synthesis route :
Syringa Aldehyde can be synthesized from para-methylbenzaldehyde, by reacting with a random chloroacetate. This step has to be followed by an acidic hydrolysis of the obtained glycidate, with a subsequent decarboxylation.
Stability :
Aldehydes can form their diethylacetal in alcoholic stability, with not great impact on their smell. They can react with nitrogen-containing compounds as Methyl Anthranilate or Indol.
Aromatic compounds are chromophorous. They can cause coloring problems, especially in alkaline bases.
Very unstable in acidic bases (detergents and antiperspirants), very alkaline bases (liquid bleach), but stable in shampoos and soaps.
Other comments :
Data not available.
Labelling
Allergens :
This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
IFRA
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is not restricted for the 51th amendment