| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | MOQ | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
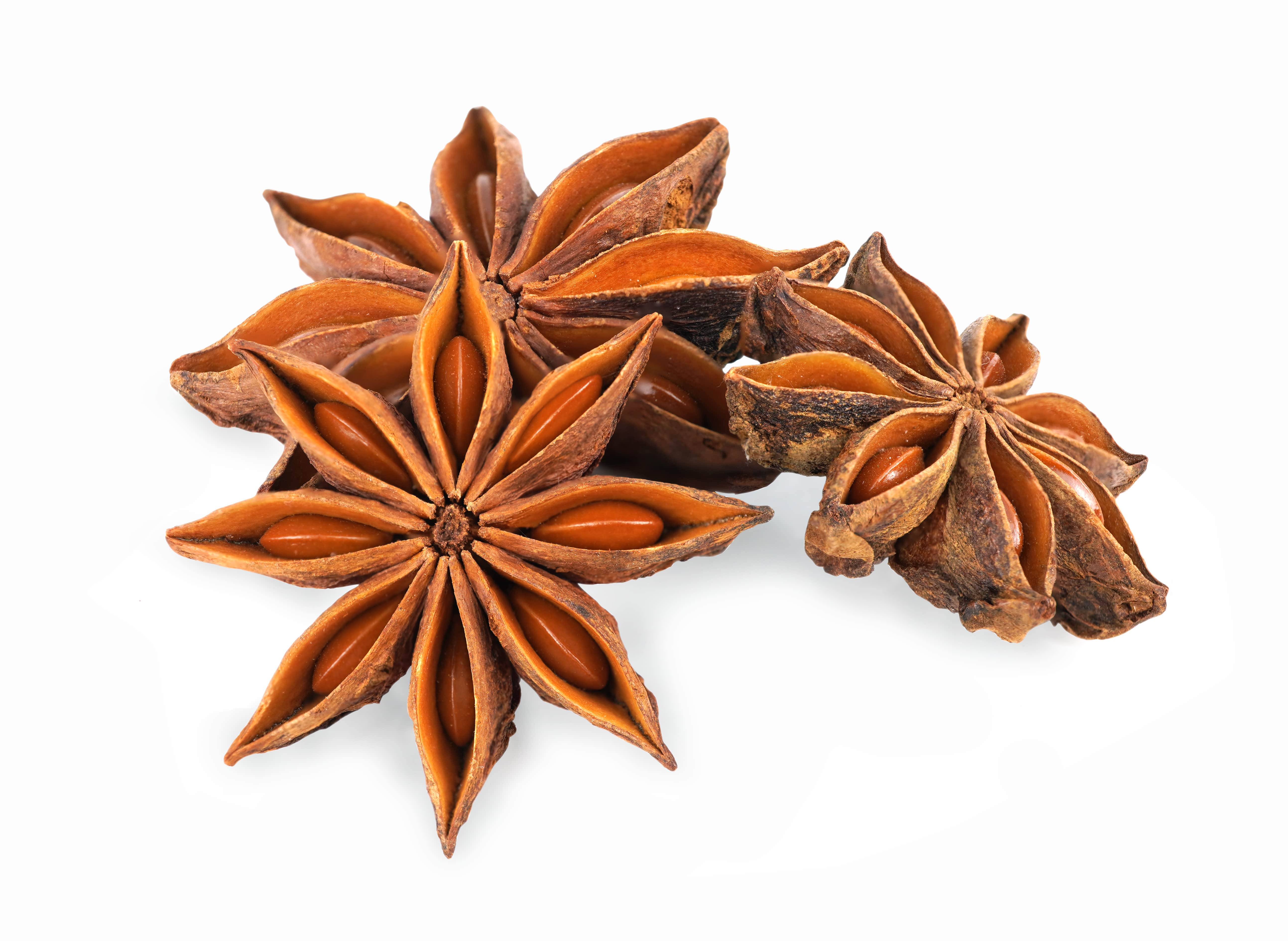
STAR ANISE SFE | 911558 |
Visit website
|
Naturals | - | ILLICIUM VERUM | - | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° :
68952-43-2 -
EINECS number :
283-518-1 -
FEMA number :
2096
-
Volatility :
Head/Heart -
Price Range :
Donnée indisponible.
Physico-chemical properties
-
Appearance :
Yellow green to brown green liquid -
Density :
0,953 - 0,993 @20°C 0,950 - 0,990 @25°C -
Refractive Index @20°C :
1.515 - 1.555 @20°C 1.512 - 1.553 @25°C -
Optical rotation :
-5° // 5° @20°C -
Vapor pressure :
Data not available. -
Flash Point :
95°C (203°F) -
Acid Value :
< 10,00
Botanical informations
Botanical name :
Illicium verum Hook.fil.
Synonyms : llicium san-ki Perr. // Illicium stellatum Makino
Botanical profile :
Star anise is the fruit of the star anise tree, from the family of the Illicaceae and the genus Illicium L.
Chemotypes :
Illisium L. is a genus containing more than fifty species.
In the F&F industry, we only use Illicium verum Hook.fil.
Illicium anisatum L., also known as Japanese star anise, is a highly toxic species that is not cultivated for essential oil extraction or culinary purposes. However, it is used as incense in East Asian countries. This variety also contains safrole and eugenol, compounds not found in Illicium verum Hook.fil., which can be used to detect adulteration, for example.
Extractions & Uses
Extraction process :
This spice is famous worldwide for its taste but also for its extracts. It owes its name to its peculiar form consisting of a woody follicle with eight carpels, each of them containing a seed.
The tree on which this star grows can reach 10 meters tall and is cultivated outside of the field at first and then, after 3 years, planted in the field, every five meters.
The propagation of a star anise crop is done by sowing seeds, directly visible in the fruits.
The harvests occur two to three times a year, in April and October. Fruits are usually picked green and sun-dried for 7 to 8 hours, until they become red-brown and lose 75% of their weight. The older the tree, the more important the harvest: a 15 year old tree can reach 20kg of fruit per year.
To collect the essential oil, seeds and bark (or seeds alone) are steam distilled for about : 48h for fresh fruits (yield: 2 to 4%) or 60h for dry fruits (yield: 8 to 9%).
Extraction can also be done with volatile solvents or with supercritical CO2 with a yield of about 10% but a higher quality of essential oil.
Uses in perfumery :
Distinguished itself from Star Anise EO by its fresher undernotes and by having lower levels of allergens.
Gives depth to fougere, citrus, aromatic and chypre notes. Also used in spicy bouquets, liquorice notes and to give naturalness to green notes.
Stability :
Data not available.
Major Components :
- Close to Star Anise SFE
- (E)-Anethole (> 85%)
- Estragole (< 2%)
- D-Limonene (2%)
- Linalool (< 1%)

Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Other comments :
The essential oil of star anise is distinguished from the green anise oil by its Fenchone content.
The adulteration of the essential oil is possible by adding synthetic Anethole (less expensive) which is the essential oil of Japanese star anise.
IFRA
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is restricted by the 51th amendment