| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | MOQ | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Huile essentielle de Pin sylvestre - 30 Gr | - |
Visit website
|
- | - | - | - | - | |
|
|
PIN SYLVESTRE | B766 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle |

|
- | Pinus sylvestris L. | Aiguille | Bulgarie |
|
|
PIN SYLVESTRE | B765 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle |

|
- | Pinus sylvestris L. | Aiguille | France |
|
|
PIN SYLVESTRE | 765 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle | - | Pinus sylvestris L. | Aiguille | Autriche |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° :
8023-99-2 -
EINECS number :
84012-35-1 -
FEMA number :
2906
-
Volatility :
Head/Heart -
Price Range :
€€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Appearance :
Colorless to pale yellow liquid -
Density :
-
Refractive Index @20°C :
Data not available. -
Optical rotation :
-
Vapor pressure :
Data not available. -
Flash Point :
Data not available. -
Acid Value :
Botanical informations
Botanical name :
Pinus sylvestris L.
Synonyms : Pinus erzeroomica Calvert ex Godr. // Pinus sylvestris f. aurea (A.H.Kent) Beissn.
Botanical profile :
Scots pine is a species of pine of the Pinaceae family and the genus Pinus L.
Chemotypes :
The Pinus L. genus includes nearly 380 different species of pine, though only a few are used in perfumery. Notable examples include:
- Pinus sylvestris L.: Scots Pine Needle Essential Oil / Scots Pine Needle Resinoid, found throughout the Northern Hemisphere
- Pinus palustris Mill.: Pine Tar Essential Oil, found mainly in the eastern United States
- Pinus pumila (Pall.) Regel: Dwarf Siberian Pine Needle Essential Oil, found mainly in eastern Russia
- Pinus pinaster Aiton: Maritime Pine Essential Oil, found mostly in Europe and southern Australia
- Pinus nigra J.F.Arnold: Black Pine Essential Oil, found mainly in Europe and the United States
White Pine (Pinus strobus), Red Pine (Pinus resinosa), Jack Pine (Pinus divaricata), and Ponderosa Pine (Pinus ponderosa) are all species native to North America.
The main distinction between a pine (Pinus L.) and a fir (Abies Mill.) lies in the arrangement of their needles: pines bear needles in clusters of two, three, or five, whereas fir needles are attached singly along the branch.
Extractions & Uses
Extraction process :
Scots pine can grow up to 40 metres high on poor, siliceous soils. The part treated to obtain the essential oil of Scots pine is its branches of needles. The tree is generally grown from July to September in Siberia. The month of harvest can have an influence on the composition of the essential oil.
Whole trees are uprooted in order to easily separate the needle branches from the wood of the tree, that is used in other industries. Generally, machines used to uproot trees also make it possible to ''shave '' the trunk and remove branches and twigs.
At the factory, the needle branches are dried in the open air for a few hours, and then introduced and compacted in the extraction tank. The water vapour for extraction is injected from the bottom of the tank to pressurize the branches with water. Extraction takes 2 to 3 hours.
The essential oil of Scots pine is obtained at the end of the process, after refrigeration of the steam, by settling the essential oil, above pine water. The extraction yield of this essential oil varies between 0.1 and 0.2%.
Often, the resin in the wood of this tree is used to extract Turpentine EO, which has a high added value and a heady smell.
Uses in perfumery :
Used in woody and masculine notes to bring out a fresh, functional, zesty and characteristic woody effect.
Stability :
Terpenes present in this essential oil are subjected to polymerization under the effect of a strong oxydation.
Major Components :
- Alpha-pinene (30 - 40%)
- Delta-3-carene (3 - 12%)
- D-Limonene (6 - 9%)
- Camphene (5 - 7%)
- Myrcene (4 - 6%)
- Beta-pinene (2 - 4%)
- Bornyl acetate (1 - 3%)
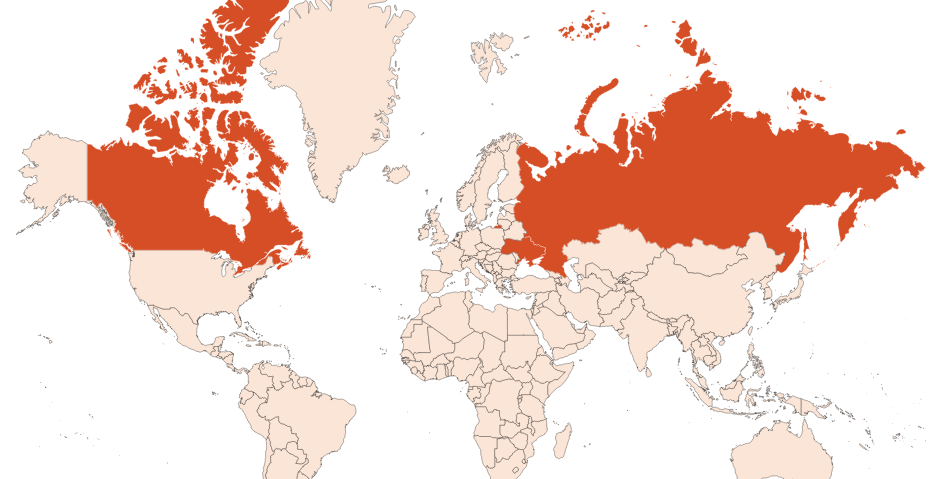
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Other comments :
The difference between a pine tree and a fir tree is made in the grouping of their needles. In the case of pine, they are grouped and attached to the branches. In the case of fir, they are independently attached to the branches.
Very often, pine essential oil and turpentine oil allow the extraction of various terpenes such as pinene, carene and many others.
Olfactively, Scots pine and Siberian pine EO are very different : Scots pine is much more zesty, close to Lime EO, while Siberian pine has a more functional smell of detergent.
IFRA
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is not restricted for the 51th amendment