Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
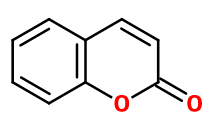
Coumarin
Balsamic Ambery > Coumarinic
Chromen-2-one ; Benzo-alpha-pyrone ; 2-oxo-1,2-benzopyran ; 1-benzopyran-2-one ; 1,2-benzopyrone ; Chromenone ; Coumarinic acid lactone ; Coumarinic anhydride ; Cumarin ; Ortho-hydroxycinnamic acid delta-lactone ; Ortho-hydroxycinnamic acid lactone ; 3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-propenoic lactone ; Tonka bean camphor

Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | MOQ | Purity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Coumarine - 30 Gr | - |
Visit website
|
- | - | - | |
|
|
COUMARINE | M_0055060 |
Visit website
|
Naturel | - | - | |
|
|
COUMARIN | - |
Visit website
|
- | 10 grs | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° :
91-64-5 -
EINECS number :
202-086-7 -
FEMA number :
Donnée indisponible. -
FLAVIS number :
Donnée indisponible.
-
JECFA number :
Donnée indisponible. -
Volatility :
Heart -
Price Range :
€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Appearance :
White solid -
Density :
1,247 -
Refractive Index @20°C :
Data not available. -
Optical rotation :
Data not available. -
Vapor pressure :
0.00127 mmHg @25°C -
Flash Point :
162°C (323,6°F)
-
Molecular formula :
C9H6O2 -
Molecular Weight :
146,14 g/mol -
Log P :
Donnée indisponible. -
Fusion Point :
71°C (159,8°F) -
Boiling Point :
297°C (566,6°F) -
Detection Threshold :
34 et 50 ppb (0,000005%)
Chemistry & Uses
Uses in perfumery :
Coumarin is a key element in the composition of oriental and fougere notes. Allows to bring a gourmand and vanillic facet to all types of accords. Good fixator.
Year of discovery :
Discovered in 1868. English chemist William Henry Perkin synthesized Coumarin for the first time, twenty years after its natural discovery by German chemist Friedrich Whöler. The industrial synthesis of Coumarin only started in 1877.
Natural availability :
Coumarin is present in several plant extracts, including Tonka Bean Absolute, Hay Absolute or sweet woodruff, of which it is the major constituent and from which it can be extracted in its natural state.
Isomerism :
Coumarin does not have any isomer used in perfumery.
Synthesis precursor :
Coumarin allows the synthesis of several perfume compounds. In a diluted alkaline medium, it can be hydrolysed to be converted to cis-2-Hydroxycinnamic acid. In a concentrated alkaline medium, at a hot temperature and in the presence of ethanol, the resulting product is trans-2-Hydroxycinnamic acid. Dihydrocoumarin is obtained by a catalytic hydrogenation of coumarin. Hydrogenation at a high temperature (392-482 °F) allows to synthesize Octahydrocoumarin.
Synthesis route :
Coumarin is synthesized from Salicylaldehyde by a Perkin synthesis. This reaction consists in reacting Salicylaldehyde with acetic anhydride in the presence of sodium acetate at a high temperature. Acetic acid also results from this reaction and is the most used method.
Stability :
Coumarin gets red in alkaline functional bases.
Other comments :
Coumarin is one of the 26 allergens in perfumery.
Its smell is similar to Dihydrocoumarin and less fruity than Octahydrocoumarin.
Its detection threshold is
IFRA
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is restricted by the 51th amendment
- Quantitative limit on the use :
-
Cat.1 Cat.2 Cat.3 Cat.4 Cat.5A B C DCat.6 0,089 % 0,08 % 0,089 % 1,5 % 0,38 % 0,11 % 0,16 % 0,035 %0,0024 % Cat.5A B C DCat.6 0,38 % 0,11 % 0,16 % 0,035 %0,0024 % Cat.7A BCat.8 Cat.9 Cat.10A BCat.11A BCat.12 0,18 % 0,18 %0,035 % 0,52 % 0,52 % 1,6 %0,035 % 0,035 %33 % Cat.10A BCat.11A BCat.12 0,52 % 1,6 %0,035 % 0,035 %33 %