| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | MOQ | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
VIOLET IG GRASSE ABS | 991521 |
Visit website
|
Naturals | - | VIOLA ODORATA | - | - | |
|
|
VIOLET LEAF EGYPT ABS | 991725 |
Visit website
|
Naturals | - | VIOLA ODORATA | - | - | |
|
|
Absolue de Feuilles de Violette - 30 gr | - |
Visit website
|
- | - | - | - | - | |
|
|
VIOLET Absolute | M_0053279 |
Visit website
|
Naturel | - | - | - | - | |
|
|
VIOLET Absolute (France) | M_0053280 |
Visit website
|
Naturel | - | - | - | - | |
|
|
VIOLET LEAF EGYPT ABS P&N | - |
Visit website
|
- | 10 grs | - | - | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° :
8024-08-6 -
EINECS number :
90147-36-7 -
FEMA number :
3110
-
Volatility :
Heart -
Price Range :
€€€€€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Appearance :
Green paste -
Density :
0,920 - 0,950 @20°C -
Refractive Index @20°C :
1.475 - 1.490 @20°C -
Optical rotation :
N/A -
Vapor pressure :
Data not available. -
Flash Point :
120°C (248°F) -
Acid Value :
Botanical informations
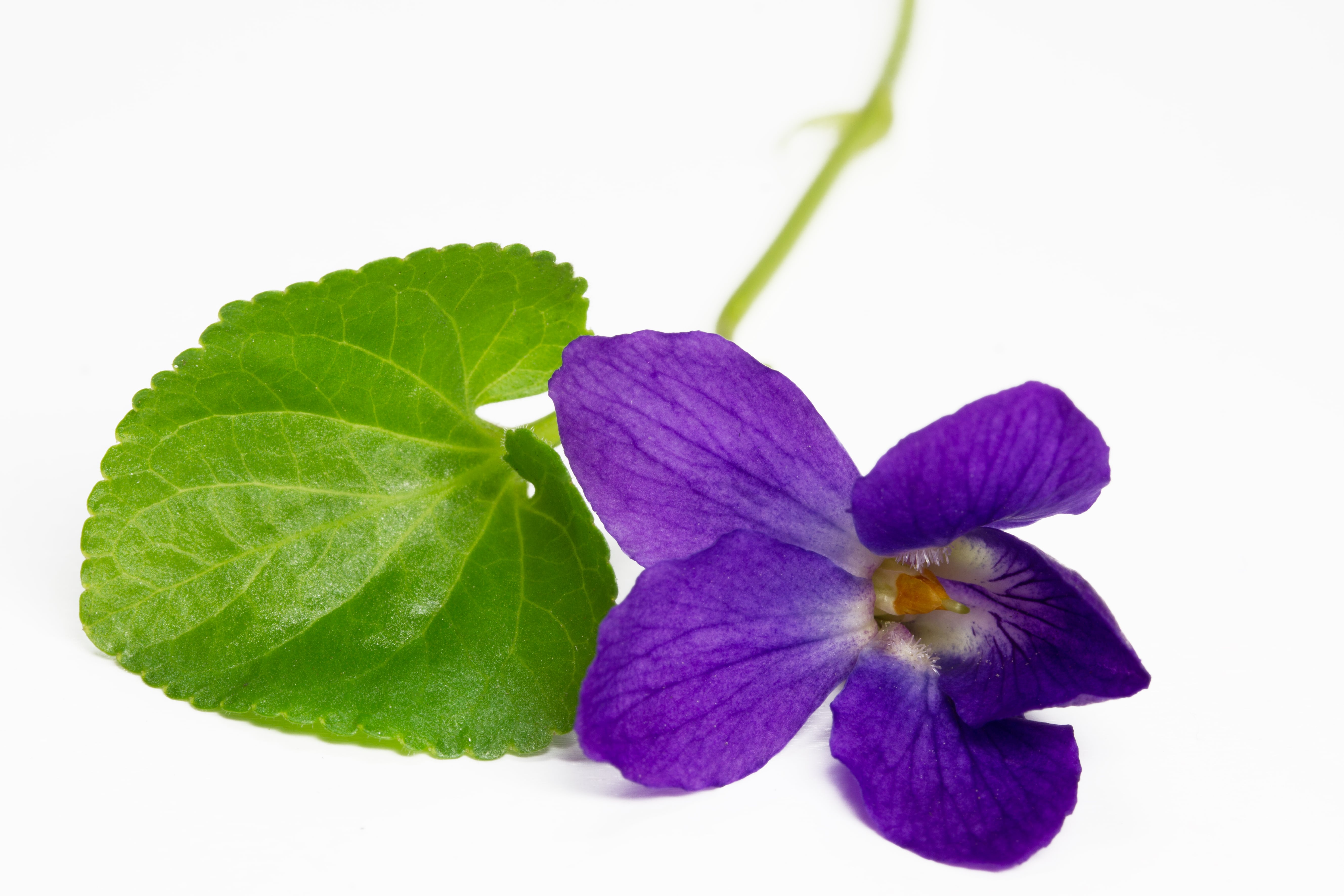
Botanical name :
Viola odorata L.
Synonyms : Viola cyclophylla Gand. // Viola vilmoriniana Delacour & Mottet
Botanical profile :
The violet is a plant of the Violaceae family, and of the genus Viola L.
Chemotypes :
The violet odorata includes two major varieties:
The violet of Parma, the most used in perfumery.
The violet Victoria, called ''Luxanne ''.
Extractions & Uses
Extraction process :
Cultivation of the violet leaves requires very fertile and fairly well drained soil. In Egypt, for example, cultivation is practiced on the Nile Delta, one of the most fertile regions in the world. Moreover, a warm climate is favorable to the plant growth. The leaf harvest is made from May to December and the leaves are cut by hand or with a sickle. An hectare of cultivation allows to cultivate 10 tons of leaves per cut (the number of cuts each year varies from 1 to 4 according to the place of harvest). The leaves are gathered in large bags and taken to the extraction plant.
The fresh leaves are placed into the extractor immediately or after a day, and extracted with a first volatile solvent such as hexane, to obtain the violet leaf concrete, in the form of a dark green paste, after evaporation of the solvent. To obtain the concrete, two extractions with hexane of two hours each, are necessary.
The extraction yield for the concrete is about 0.09%. Once the concrete with hexane is obtained, it is diluted in alcohol to precipitate the waxes by glazing at 32 °F. The absolute is obtained after filtration and evaporation of the alcohol. Sometimes, the violet leaf extraction result is subject to a distillation to be bleached, without a great olfactory impact.
Uses in perfumery :
Used in luxury perfumery for green, leather, iridescent, violet and mimosa notes. Brings a green facet to Tuberose Absolute. Useful in fruity-melon, watermelon, cucumber, marine and tea notes. Supports woody notes.
Stability :
Solubility issues in perfumes
Stable oil in perfumes and in diverse functional bases
Major Components :
- Linolenic acid (≈2%)
- Linoleic acid (≈1%)
- (2E,6Z)-Nonadienal (≈1%)
- 3-Octenol (≈0,5%)
- (Z)-3-hexenyl acetate (≈0,5%)
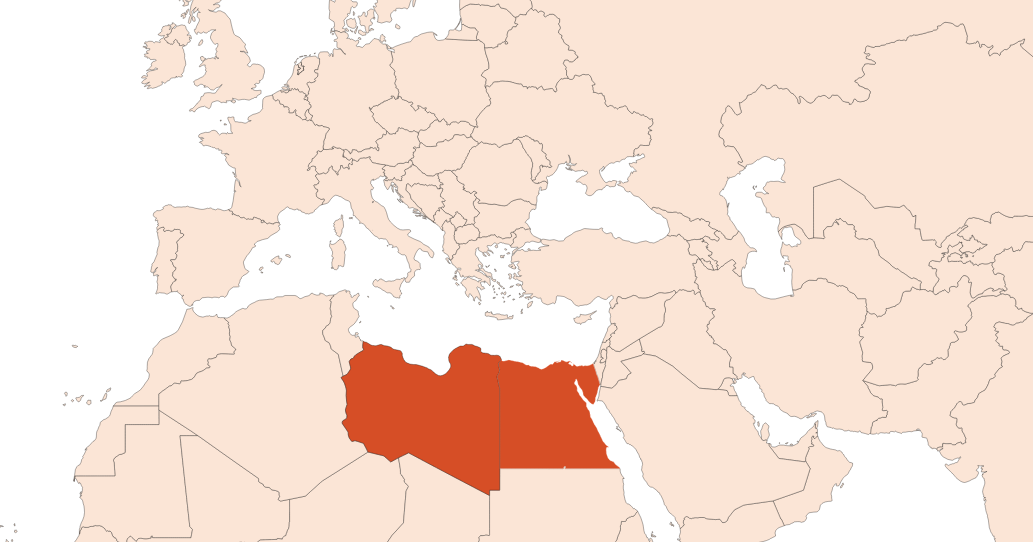
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Other comments :
The violet leaf is the only extractable part of the violet. The flowers are mute: they give almost no result when they are extracted. By the way, leaves do not smell like the flowers.
In the Middle Ages, the violet was considered an aphrodisiac plant, whose delicate flowers were part of the pillow stuffing and predisposed to love.
IFRA
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is restricted by the 51th amendment