Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | MOQ | Purity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Natural Methyl Cinnamate | AM-002 |
Visit website
|
Natural |



|
25 Kgs | 100 |
|
|
METHYL CINNAMATE | 21009 |
Visit website
|
Molecule | - | - | |
|
|
METHYL CINNAMATE | - |
Visit website
|
- | 10 grs | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° :
103-26-4 -
EINECS number :
203-093-8 -
FEMA number :
2698 -
FLAVIS number :
Donnée indisponible.
-
JECFA number :
Donnée indisponible. -
Volatility :
Base -
Price Range :
€€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Appearance :
White crystals -
Density :
1,042 -
Refractive Index @20°C :
1,577 -
Optical rotation :
Data not available. -
Vapor pressure :
0.0112 mmHg @25°C -
Flash Point :
123°C (253,4°F)
-
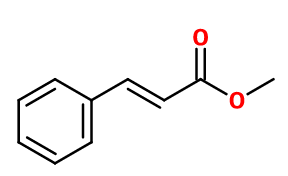
Molecular formula :
C10H10O2 -
Molecular Weight :
162,19 g/mol -
Log P :
Donnée indisponible. -
Fusion Point :
37°C (98,6°F) -
Boiling Point :
255°C (491°F) -
Detection Threshold :
Donnée indisponible.
Chemistry & Uses
Uses in perfumery :
Methyl Cinnamate is used mainly to create oriental accords (vanilla, balsams, leather) or floral notes such as rose, carnation or hyacinth.
Year of discovery :
Data not available.
Natural availability :
Methyl Cinnamate is present in various plants, starting with plants of the genus Alpinia, from the zingibiraceae family (same family as ginger), of which it can represent up to 80% of the composition of the essential oil. It is also present at more than 50% in the essential oil of Ocimum canum, a plant of the lamiaceae family, looking like clary sage. Methyl Cinnamate can therefore be extracted from these raw materials.
Isomerism :
The double bond of Methyl Cinnamate gives rise to two possible diastereoisomers. Both have a relatively similar smell. The racemic mixture of the two isomers is generally used in perfumery.
Synthesis precursor :
Methyl Cinnamate is not a precursor to the synthesis of another compound of olfactory interest.
Synthesis route :
Methyl Cinnamate can be synthesized in two ways. The first is a conventional acidic esterification between Cinnamic Acid and methanol. The second is a Claisen condensation, that consists in reacting Benzaldehyde with Methyl acetate in the presence of sodium.
Stability :
Molecule encountering some great solubilization difficulties. May form cinnamic acid through time.
Tends to get a yellow color through time.
Other comments :
Methyl Cinnamate is one of the most powerful cinnamic esters. It is much more powerful than Benzyl Cinnamate for example.
IFRA
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is not restricted for the 51th amendment