| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | MOQ | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
GENEVRIER | B435 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle |

|
- | Juniperus communis L. | Rameau | France |
|
|
GENEVRIER | 437 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle | - | Juniperus communis L. | Rameau | Albanie |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° :
8002-68-4 -
EINECS number :
616-801-9 -
FEMA number :
2604
-
Volatility :
Head/Heart -
Price Range :
Donnée indisponible.
Physico-chemical properties
-
Appearance :
Colorless liquid -
Density :
-
Refractive Index @20°C :
Data not available. -
Optical rotation :
-
Vapor pressure :
Data not available. -
Flash Point :
Data not available. -
Acid Value :
Botanical informations
Botanical name :
Juniperus communis L.
Synonyms : Juniperus caucasica Fisch. ex Godr. // Juniperus nana f. canadensisaurea Beissn.
Botanical profile :
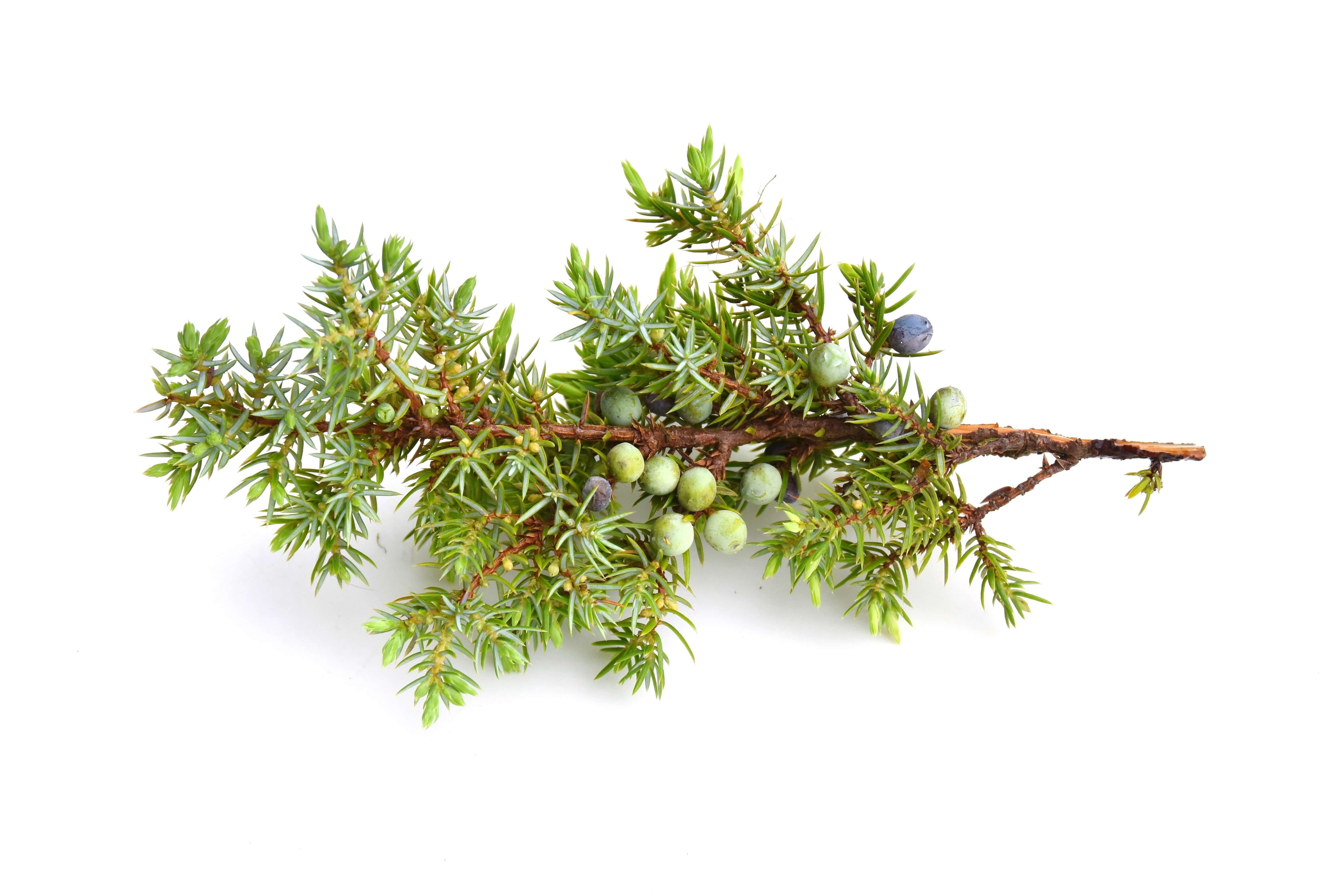
Juniper belongs to the Cupressaceae family and to the Juniperus L. genus.
Chemotypes :
There are currently, around 600 known species of conifers, including the Juniperus L. genus.
Several species from this genus are used in perfumery, the most common being:
- Juniperus communis L.: Juniper berry oil - Juniper leaves oil
- Juniperus virginiana L.: Cedarwood Virginia oil
- Juniperus mexicana Schiede.: Cedarwood Texas oil
- Juniperus oxycedrus L.: Cade oil
Other notable species include Alpine Juniper (Juniperus alpina L.), native to the Alps and Corsica and cultivated for its branches, Himalayan Juniper (Juniperus indica L.), and Spanish Juniper (Juniperus thurifera L.).
Extractions & Uses
Extraction process :
Juniper (Juniperus Communis) is a tree containing essential oil in its branches as well as in its berries. The production of Juniper leaves EO is much rarer than Juniper Berry EO. This is because the essential oil from the berries is a by-product of the production of Gin, the popular spirit. However, to obtain the essential oil from the branches, the process is different as the extraction is done on the branches AND the berries by hydrodistillation. The yield is between 2 and 5%. This makes a difference to the process because the presence of branches prevents the production of gin, the main reason for the cultivation of this tree.
Uses in perfumery :
Data not available.
Stability :
The esters identified in this raw material can form their corresponding acid in stability tests
The terpenes identified in this raw material can polymerize when they are oxidized-
Caution: this EO is not soluble in alcohol- making it very complex to use in fine perfumery-
Major Components :
Data not available.
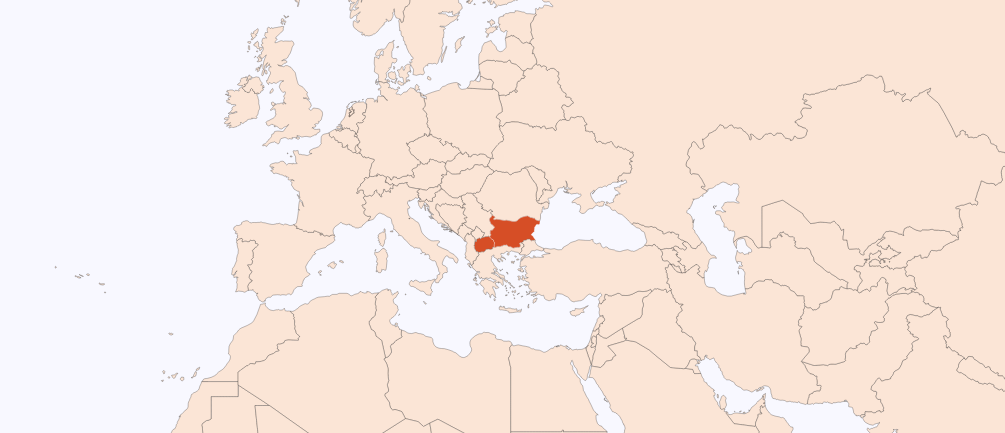
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Other comments :
The juniper berries are part of the composition of Gin.
IFRA
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is not restricted for the 51th amendment