| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | MOQ | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
LIATRIX ABS SUBST | 954904 |
Visit website
|
Naturals | - | - | - | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° :
68602-86-8 -
EINECS number :
272-627-7 -
FEMA number :
Donnée indisponible.
-
Volatility :
Base -
Price Range :
€€€€€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Appearance :
Green paste -
Density :
-
Refractive Index @20°C :
Data not available. -
Optical rotation :
-
Vapor pressure :
Data not available. -
Flash Point :
Data not available. -
Acid Value :
Botanical informations
Botanical name :
Carphephorus odoratissimus (J.F.Gmel.) H.J.-C.Hebert
Synonyms : Chrysocoma odoratissima (Walter) J.F.Gmel. // Liatris odoratissima (J.F.Gmel.) Michx.
Botanical profile :
Liatrix is a plant belonging to the Asteraceae family and the genus Carphephorus Cass.
The Asteraceae family is one of the most important in perfumery, including plants such as Artemisia species (absinthe, armoise, tarragon, davana), as well as tagetes, tansy, and immortelle.
Chemotypes :
The genus Carphephorus Cass. includes around 8 species, of which only the Deertongue introduced here is used in perfumery.
Extractions & Uses
Extraction process :
In the United States, Liatrix fields are perennial and grow by collecting and sowing the seeds of the plant. The seeds must be collected once the plant is dry, after a few weeks and must have a black and dry appearance.
For their use in perfumery, liatrix leaves are collected by hand and dried in the sun. Then, the most volatile molecules evaporate from the leaves and only the heavier molecules remain. This is why the smell of liatrix is very coumarin and hot.
The extraction with hexane gives a concrete after the plants are removed from the extractor and the solvent has evaporated. This first extract is pasty because it contains waxes. A treatment with alcohol is made to obtain the absolute by precipitating the waxes, which are insoluble in the alcohol, and by subjecting the concrete to a glazing process at 32 °F. After filtration of the opaque mixture, the alcohol is evaporated and the liatrix absolute is obtained.
Uses in perfumery :
Used in luxury perfumery for fougere, amber, blond tobacco notes.
Stability :
Solubility issues in perfumes
Stable oil in perfumes and in diverse functional bases
Major Components :
- Coumarin (50 - 75%)
- Dihydrocoumarin (5 - 10%)
- Benzyl benzoate (5 - 10%)
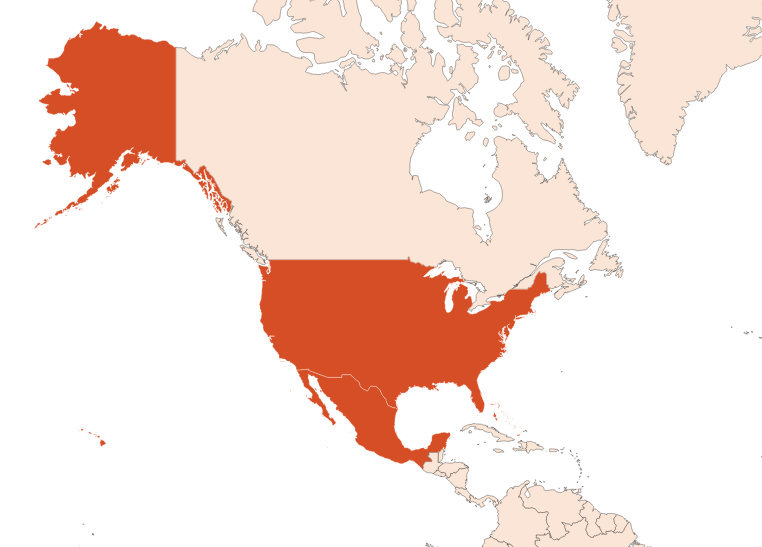
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Other comments :
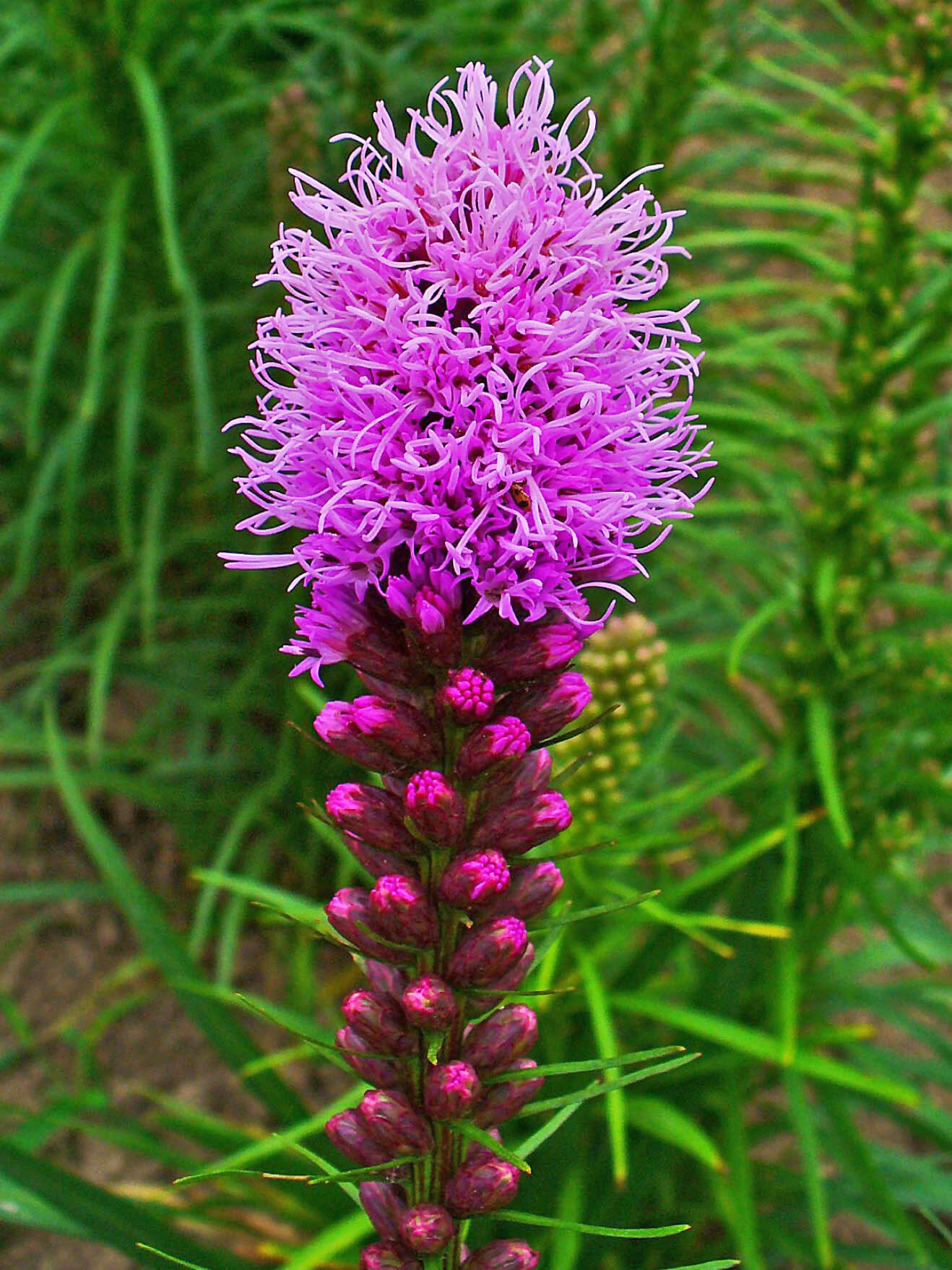
The liatrix is native to the United States. Its flowers form clumps at the end of a long stem whose leaves are extracted in perfumery.
Liatrix often comes in the composition of the hay, also used in perfumery. It is of interest as its scent is coumarinic and herbaceous.
Liatrix is also used to aromatize tobacco.
IFRA
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is restricted by the 51th amendment