| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | MOQ | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
CISTUS ABS | 925094 |
Visit website
|
Naturals | - | CISTUS LADANIFERUS | - | - | |
|
|
CISTUS ABS TYPE NAT | 925084 |
Visit website
|
Naturals | - | - | - | - | |
|
|
CISTUS ABS VULCAIN | 925090 |
Visit website
|
Naturals | - | CISTUS LADANIFERUS | - | - | |
|
|
Absolue de Ciste - 30 gr | - |
Visit website
|
- | - | - | - | - | |
|
|
CISTE | F0779 |
Visit website
|
Absolue | - | Cistus ladaniferus L. | Feuille, Rameau | Espagne | |
|
|
CISTE | F0850 |
Visit website
|
Concrète | - | Cistus ladaniferus L. | Feuille, Rameau | Espagne | |
|
|
CISTE | F0940 |
Visit website
|
Eau concentrée | - | Cistus ladaniferus L. | Feuille, Rameau | Espagne | |
|
|
CISTE 70%/TEC | E1264 |
Visit website
|
Absolue | - | Cistus ladaniferus L. | Feuille, Rameau | Espagne |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° :
8016-26-0 -
EINECS number :
934-780-7 -
FEMA number :
2608
-
Volatility :
Base -
Price Range :
Donnée indisponible.
Physico-chemical properties
-
Appearance :
Brown resin -
Density :
-
Refractive Index @20°C :
Data not available. -
Optical rotation :
-
Vapor pressure :
Data not available. -
Flash Point :
Data not available. -
Acid Value :
Botanical informations
Botanical name :
Cistus ladanifer L.
Synonyms : Cistus ladaniferus L. // Cistus ladanifer f. immaculatus Dans.
Botanical profile :
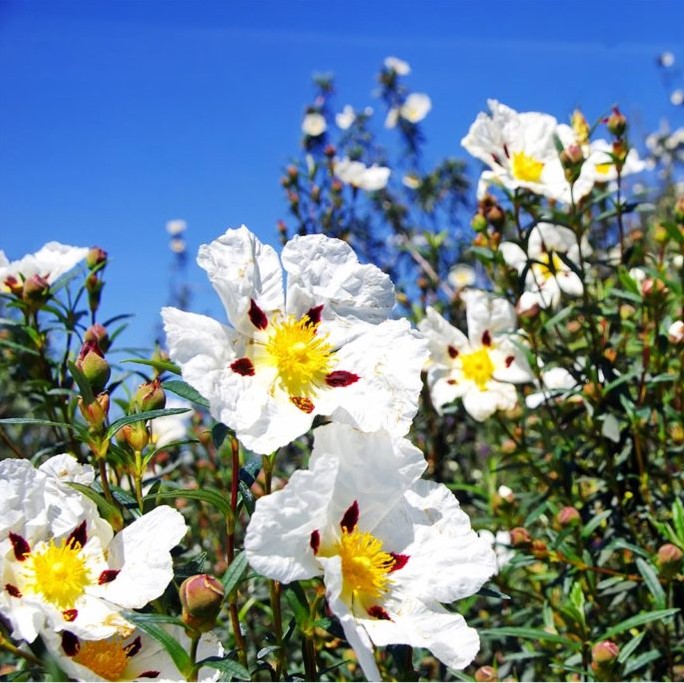
The cistus belongs to the Cistaceae family and to the genus Cistus L.
Chemotypes :
The genus Cistus L. includes about 20 different species, the majority of which exudes fragrant gum.
Among these, the most used are:
Cistus ladaniferus var. albiflorus, var. maculatos, var. stenoiphyllus, which produce the resin used in perfumes.
Cistus creticus L., with rose to purple petals, surronding a tuft of stamens.
Cistus salviifolius L., with white petals.
Cistus parviflorus Lam., with pale rose petals.
Extractions & Uses
Extraction process :
In April, Cistus ladaniferus fields are covered with the famous white flowers, but they don't smell and are very delicate (they only last a few days). It is necessary to wait a few months, around May-June, for a new shoot to appear. This new branch protects itself from the sun - and from the summer heat of southern Spain - by secreting a very fragrant viscous gum. We use the latter in perfumery.
In July, from dawn to noon, new branches are cut with a sickle, bundled and taken to the factory to extract the gum. It will then be necessary to wait another 3 years to harvest the cistus again.
To obtain the resinoid, the gum is treated in a soda solution for extraction with a 3 to 5% yield. After filtration, an acid treatment is carried out. A pasty product is recovered by skimming and distilled to dry it. The paste is finally treated with alcohol, then filtered to remove insoluble compounds. A ''labdanum alcohol resinoid '' is then obtained.
Several reprocessing are possible on the cistus absolute, to remove insoluble compounds or colour. Such rectification has no olfactory impact.
Uses in perfumery :
Data not available.
Stability :
Solubility issues in perfumes
The terpenes identified in this raw material can polymerize when they are oxidized
Major Components :
Data not available.
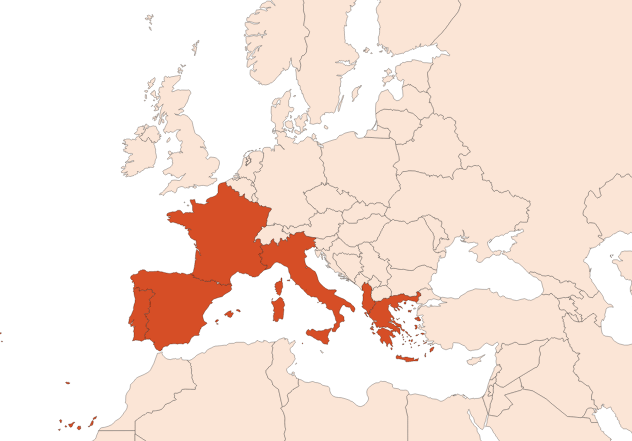
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Other comments :
Data not available.
IFRA
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is restricted by the 51th amendment