| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | MOQ | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
CHAMOMILE BLUE EO | 919030 |
Visit website
|
Naturals | - | CHAMOMILLA RECUTITA,MATRICARIA CHAMOMILLA L. | - | - | |
|
|
Camomile Oil German | - |
Visit website
|
Essential Oil | - | Matricaria recutita | - | - | |
|
|
Huile essentielle de Camomille bleue - 30 gr | - |
Visit website
|
- | - | - | - | - | |
|
|
CHAMOMILE BLUE EO | - |
Visit website
|
- | 10 grs | - | - | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° :
8002-66-2 -
EINECS number :
282-006-5 -
FEMA number :
2273
-
Volatility :
Heart -
Price Range :
€€€€€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Appearance :
Blue liquid -
Density :
For Egyptian chemotype : 0,910 - 0,970 @20°C For Hungarian : 0,910 - 0,950 @20°C -
Refractive Index @20°C :
1.499 - 1.508 @20°C -
Optical rotation :
-
Vapor pressure :
Data not available. -
Flash Point :
Data not available. -
Acid Value :
Botanical informations
Botanical name :
Data not available.
Botanical profile :
Blue chamomile is a plant belonging to the Asteraceae family and the Matricaria L. genus.
The Asteraceae family is one of the most important in perfumery, including genera like Artemisia (such as Wormwood, Armoise, Tarragon, Davana), as well as Tagetes, Tansy, and Immortelle.
Chemotypes :
There are several varieties of chamomiles, some of which are only used in perfumery:
Matricaria chamomilla L.: Chamomile blue oil, characterized by its blue hue (from a high chamazulene content), is also extensively used in perfumery.
Chamaemelum nobile (L.) All : Roman chamomile, whose essential oil grown around the Mediterranean is also widely used in perfumery.
Harc
Produced in smaller amounts, we can also identify:
Anthemis cotula L. : Stinking chamomile, is renowned for its very powerful and unpleasant smell.
Anthemis tinctoria L. : Yellow chamomile, is a yellow variety, grown in Europe and West Asia.
Ormenis multicaulis L. : Moroccan wild chamomile, grown for its essential oil in the Mediterranean basin. It has a fruity and green note.
Extractions & Uses
Extraction process :
The harvest of chamomile is made with a harvester.
Chamomiles are distilled in two ways: traditionally or in a truck box. Traditional distillation involves harvesting the chamomile with its stems without grinding it. The fresh plant is left outside to dry in the sun, before it is extracted classically, by steaming in distillation tanks. Truck box distillation consists in harvesting chamomile and its stem with a harvester by grinding it. The chamomile is extracted inside the harvest box, with a water vapor entry and an exit towards a coolant, where the essential oil is collected.
Traditional distillation gives a warmer and herbaceous scent, as both green and volatile molecules have evaporated during the drying step.
The extraction yield of blue chamomile is between 3 and 8 ‰.
The essential oil of blue camomile can be distilled to be bleached, without a great olfactory deterioration.
Uses in perfumery :
Used in fine fragrance in fougere, rose, dried fruits, tea and in association with sagebrush.
Stability :
Solubility issues in perfumes
Can fade through time and get a brownish colour
The terpenes identified in this raw material can polymerize when they are oxidized
Major Components :
- For Egyptian cultivar :
- Alpha-bisabolol oxide A (35 - 50%)
- (E)-Beta-farnesene (15 - 35%)
- Alpha-bisabolol oxide B (2 - 8%)
- Bisabolone oxide A (2 - 6,5%)
- Chamazulene (2 - 5%)
- Alpha-bisabolol (1 - 10%)
- For Hongrian cultivar :
- (E)-Beta-farnesene (20 - 51%)
- Alpha-bisabolol (15 - 40%)
- Chamazulene (5 - 22%)
- Alpha-bisabolol oxide A (2 - 27%)
- Alpha-bisabolol oxide B (2 - 21%)
- Bisabolone oxide A (1 - 4%)
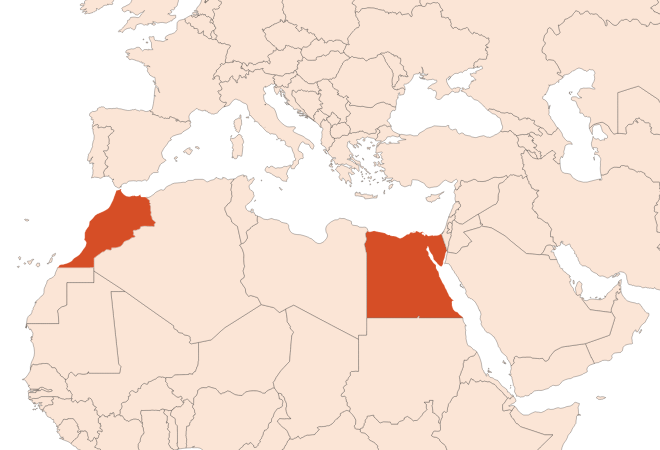
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Other comments :
The compound that gives the oil its blue colour is called chamazulene. Over time, the blue colour tends to disappear into an alcoholic base and give way to a browner hue.
Adulteration is possible using low cost Bisabolol, extracted from a shrub called Candeia (Vanillosmopsis erythropappa), known for its high Bisabolol content.
IFRA
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is not restricted for the 51th amendment