| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | MOQ | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Absolue de Champaca - 30 gr | - |
Visit website
|
- | - | - | - | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° :
94333-99-0 -
EINECS number :
305-079-8 -
FEMA number :
Donnée indisponible.
-
Volatility :
Heart/Base -
Price Range :
€€€€
Physico chemical properties
-
Appearance :
Yellow to orange liquid -
Density :
-
Refractive Index @20°C :
Data not available. -
Optical rotation :
-
Vapor pressure :
Data not available. -
Flash Point :
Data not available. -
Acid Value :
Botanical informations
Botanical name :
Data not available.
Botanical profile :
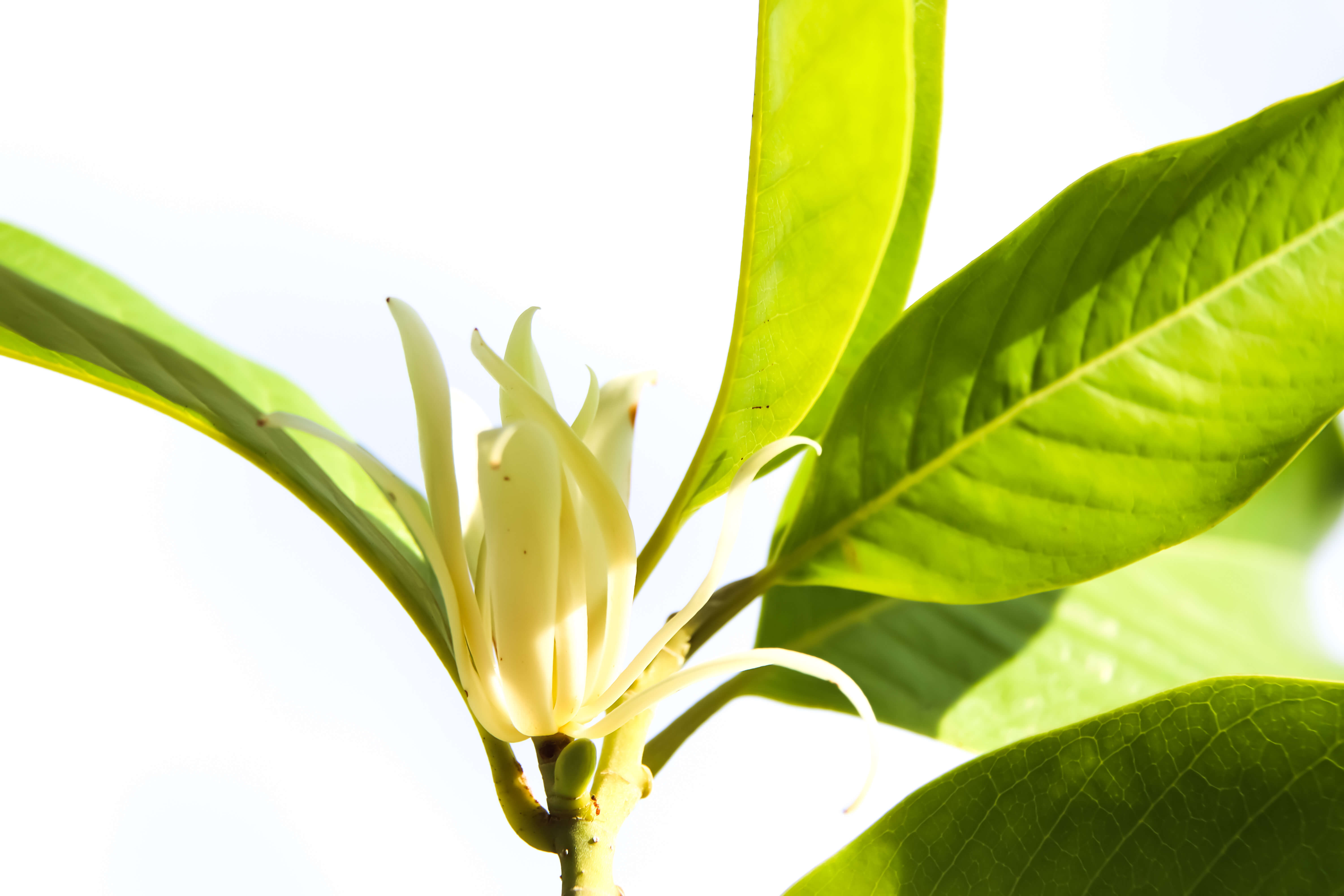
Champaca is a flower belonging to the Magnoliaceae family and the Magnolia Plum. ex L. genus.
Chemotypes :
The Magnolia Plum. ex L. genus groups close to 500 species. Among them, we can highlight:
Magnolia ×alba (DC.) Figlar : Michelia alba flower oil, from Java island (Indonesia) with linalool rich white flowers.
Magnolia champaca (L.) Baill. ex Pierre : Champaca absolute). Cultivated mainly in South Asia, it provides an essential oil and an absolute rich in (E)-beta-ionone.
Magnolia figo (Lour.) DC. from China, low volume
Magnolia maudiae var. platypetala (Hand.-Mazz.) Sima, ou magnolia de Chine, dont l'absolue est riche en Benzoate de méthyle et en Acétophénone.
Extractions & Uses
Extraction process :
Champaca is a shrub that is no more than ten metres high. Its cultivation is perpetuated by sowing seeds, obtained from the fruits. Any type of soil, but in a warm climate, can be used to cultivate champaca.
Cultivation is generally done in summer, until early fall. Once harvested, the fresh flowers are extracted using a first volatile solvent such as hexane. This first extraction, which lasts a few hours under heat, gives leads to a concrete of champaca, with a waxy texture, after removing the flowers from the extractor and evaporating the extraction solvent. A second extraction is necessary in alcohol, a solvent in which the waxes of the concrete are not soluble. By a chilling process, consisting in gradually cooling this mixture, the waxes are precipitated, filtered and the solvent is evaporated, to recover only the absolute of the champaca flower.
The leaves of champaca, distilled in Java, its island of origin, have a strong basil smell.
Uses in perfumery :
Allows to nuance white flowers notes, with a warm and cinnamic side.
Stability :
Esters found in this extract my form their corresponding acid through time.
Methyl Anthranilate present in the extract can form Schiff bases by reaction with aldehydes in perfumes.
Major Components :
- Phenyl ethyl alcohol (20 - 30%)
- Methyl linoleate (10 - 15%)
- Methyl anthranilate (4 - 5%)
- Benzyl acetate (3 - 5%)
- Beta-ionone (3 - 4%)
- Indole (2 - 3%)
- Linalool (≈2%)
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Other comments :
Champaca absolute can be used to extract Methyl Anthranilate in its natural state.
Regulations & IFRA
Allergens :
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is restricted by the 51th amendment
Annexe I :
Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Cinnamic alcohol | 104-54-1 | 0,02 |
| Eugenol | 97-53-0 | 0,55 |
| Isoeugenol | 97-54-1 | 0,03 |
| Methyl eugenol | 93-15-2 | 0,01 |
| Benzyl benzoate | 120-51-4 | 0,53 |
| Benzyl alcohol | 100-51-6 | 0,64 |
| Benzyl cyanide | 140-29-4 | 1 |
| trans-trans-Farnesol | 106-28-5 | 0,01 |